Photosynthesis (Chapter 8)
Photosynthesis is the process by which organisms convert light energy into chemical energy that all organisms can use directly, or indirectly, to carry out life functions.
| ch8.pdf |
|
8.1 Energy and Life
ATP can easily release and store energy by breaking and re-forming the bonds between its phosphate groups. This characteristic of ATP makes it exceptionally useful as a basic energy source for all cells. In the process of photosynthesis, plants convert the energy of sunlight into chemical energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates. |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
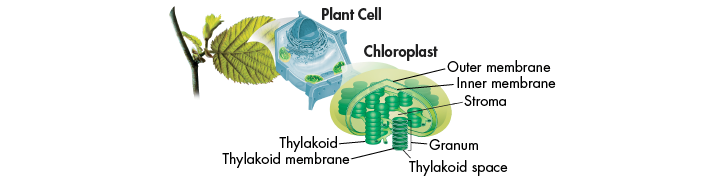
8.2 Photosynthesis: An Overview
Photosynthetic organisms capture energy from sunlight with pigments. An electron carrier is a compound that can accept a pair of high-energy electrons and transfer them, along with most of their energy, to another molecule. Photosynthesis uses the energy of sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide (reactants) into high-energy sugars and oxygen (products). |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
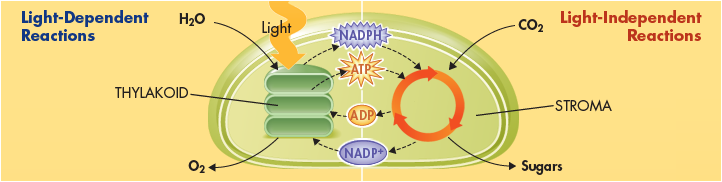
8.3 The Process of Photosynthesis
The light-dependent reactions use energy from sunlight to produce oxygen and convert ADP and NADP+ into the energy carriers ATP and NADPH. During the light-independent reactions, ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions are used to produce high-energy sugars. Among the most important factors that affect photosynthesis are temperature, light intensity, and the availability of water. |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|